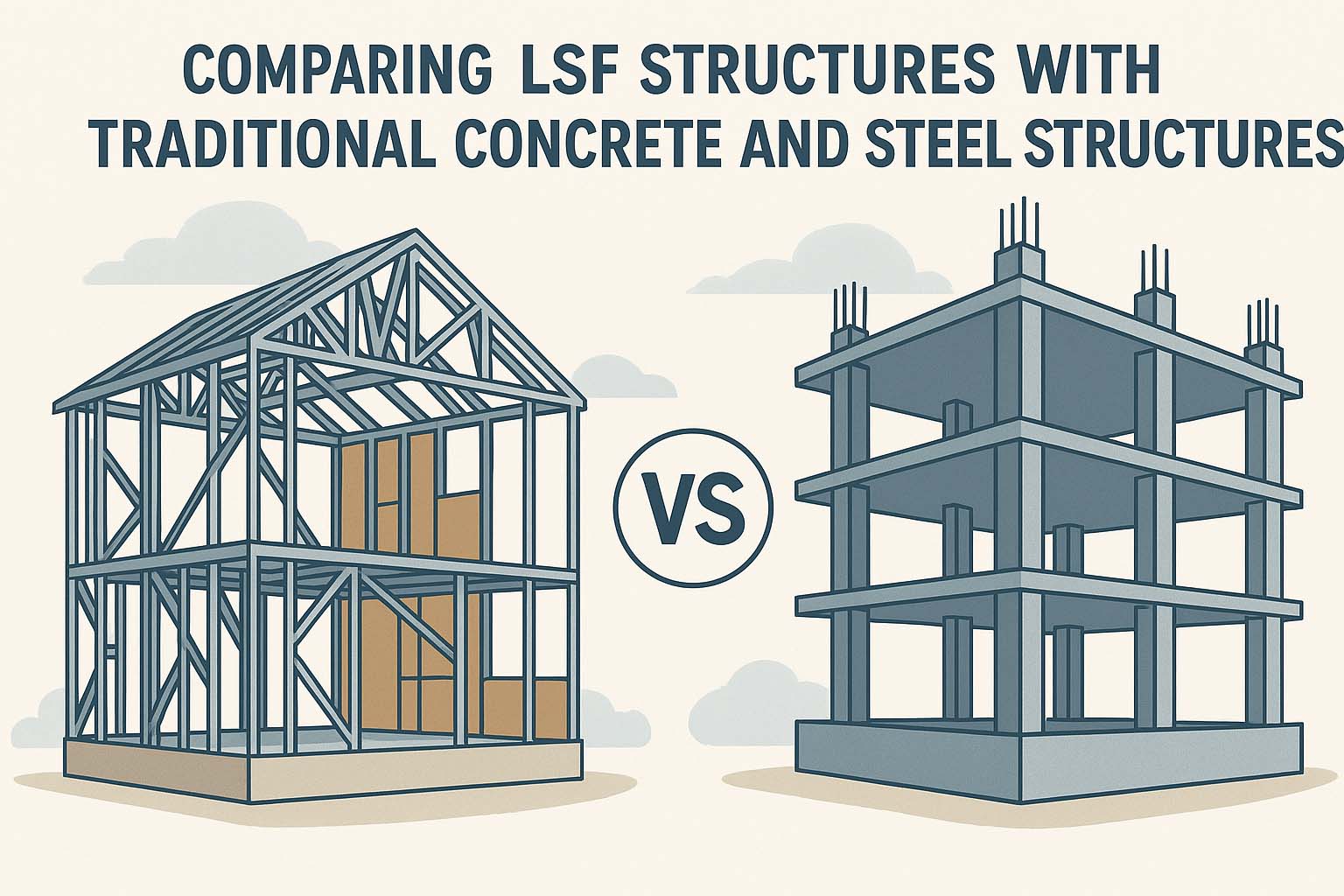
In recent years, LSF (Light Steel Frame) structures have gained significant popularity as a modern alternative to traditional construction methods using concrete or hot-rolled steel. With increasing demands for faster, more efficient, and sustainable building solutions, LSF systems offer distinct advantages. Below, we compare LSF with conventional concrete and steel structures across several key aspects:
1. Weight and Material Efficiency
One of the most noticeable differences is weight. LSF structures are significantly lighter than both concrete and hot-rolled steel buildings. This lightweight characteristic reduces foundation loads, leading to cost savings in foundation design and making LSF ideal for areas with weak soil or retrofit projects where additional load capacity is limited.
2. Speed of Construction
LSF systems are prefabricated and delivered ready to assemble, allowing for extremely fast on-site installation. While concrete requires time for curing and hot-rolled steel demands complex welding and bolting, LSF structures can be assembled in a matter of days or weeks, significantly reducing project timelines.
3. Seismic Performance
Thanks to their light weight and ductility, LSF structures perform exceptionally well in seismic zones. The reduced mass minimizes inertial forces during an earthquake, and the steel frame provides a flexible yet strong skeleton that can absorb and dissipate seismic energy more effectively than rigid concrete structures.
4. Accuracy and Quality Control
LSF components are typically produced using CNC-controlled roll-forming machines, resulting in high dimensional accuracy. Unlike concrete which is subject to site variability, or heavy steel which often requires on-site adjustments, LSF offers consistent quality with fewer errors during assembly.
5. Environmental Impact
LSF construction generates less on-site waste, consumes fewer natural resources, and is fully recyclable. Compared to concrete, which has a high carbon footprint, LSF is a more sustainable choice. Moreover, steel framing is compatible with high-performance insulation systems, contributing to energy-efficient buildings.
6. Cost Considerations
Although the initial material cost of LSF may be slightly higher than traditional concrete, the overall project cost is often lower due to faster construction, reduced labor, smaller foundations, and minimized waste. It also offers long-term savings in energy consumption and maintenance.
Conclusion
While each structural system has its own strengths and appropriate use cases, LSF stands out for projects requiring speed, flexibility, and high seismic resilience. It's a modern solution that aligns with current construction trends—lightweight, fast, precise, and environmentally responsible.
Light Steel Frame (LSF) construction is gaining global popularity due to its efficiency, lightweight nature, and versatility. However, proper structural performance and safety depend heavily on adherence to well-established design codes and standards. Here are the most important international codes that guide the design, analysis, and fabrication of LSF structures:
1. AISI Standards (North America)
The American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) provides comprehensive guidelines for cold-formed steel design, which are widely used in the U.S. and many other countries. Key documents include:
• AISI S100: North American Specification for the Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members
• AISI S240: North American Standard for Cold-Formed Steel Structural Framing
• AISI S400: Seismic Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Systems
These standards are often referenced in U.S. building codes and are critical for both structural and seismic design.
2. Eurocode (Europe)
In Europe, Eurocode 3 is the primary standard for steel structure design. For cold-formed steel, the relevant part is:
• EN 1993-1-3: Design of steel structures – Supplementary rules for cold-formed members and sheeting
This standard covers the calculation of load-bearing capacity, stability, and detailing for cold-formed profiles used in LSF systems.
3. AS/NZS Standards (Australia and New Zealand)
Australia and New Zealand have jointly developed a set of standards tailored to their construction environment:
• AS/NZS 4600: Cold-Formed Steel Structures
• NASH Standards: Published by the National Association of Steel-Framed Housing, these are practical guidelines specifically developed for residential and low-rise steel framing in Australia.
The AS/NZS 4600 standard is recognized internationally for its clarity and precision in cold-formed steel design.
4. BS 5950 (United Kingdom - Legacy Standard)
Although the UK has transitioned to Eurocodes, BS 5950 Part 5 was historically used for the design of cold-formed thin gauge sections. Some designers in former British territories may still refer to this standard.
5. SANS Standards (South Africa)
• SANS 10162-2: Structural Use of Steel - Part 2: Limit-State Design of Cold-Formed Steelwork
This standard is commonly used in South African engineering practice and is based on principles similar to AISI and AS/NZS standards.
Conclusion
Using the correct design code is essential for the safe and efficient performance of any LSF structure. While the core engineering principles are similar, each code has its own specific approach to design limits, safety factors, and detailing rules. Designers should always ensure they are using the standard that is recognized and approved in the region where the project is located.
Whether you are building a residential home, commercial facility, or modular structure, compliance with these standards ensures durability, safety, and long-term value.
When it comes to building a villa or a second home, speed, efficiency, and long-term value matter. Light Steel Frame (LSF) construction offers a modern alternative to traditional building methods, combining durability with cost-effectiveness — making it an ideal solution for residential projects, especially in remote or scenic areas.
1. Fast Construction with Minimal Disruption
LSF systems are prefabricated and assembled with precision, significantly reducing on-site labor and construction time. This is particularly beneficial for villas or second homes built in countryside or coastal areas where accessibility may be limited.
2. Lightweight but Strong
Despite being lightweight, LSF structures are engineered to meet strict structural requirements. They offer excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making them safe and stable even in areas prone to earthquakes or strong winds.
3. Excellent Thermal and Acoustic Performance
Modern LSF systems incorporate high-performance insulation materials, ensuring thermal comfort in both hot and cold climates. They also provide good acoustic insulation — an important feature for peaceful retreats.
4. Flexible Architectural Design
LSF construction allows for creative and customizable designs. Whether you prefer a modern minimalist villa or a traditional style home, LSF adapts easily to your vision without structural limitations.
5. Eco-Friendly and Energy-Efficient
Steel is recyclable, and LSF systems generate minimal construction waste. Additionally, the energy efficiency of these homes contributes to lower utility costs and a smaller environmental footprint over time.
6. Lower Maintenance Over Time
Unlike wood or masonry, LSF structures do not suffer from issues like rot, termites, or cracking. This results in lower maintenance costs and longer lifespan — a key advantage for vacation homes that may be unoccupied for extended periods.
Conclusion:
Choosing LSF for your villa or second home means choosing a modern, sustainable, and practical building solution. It’s not just about faster construction — it's about better performance, greater design freedom, and long-term peace of mind.
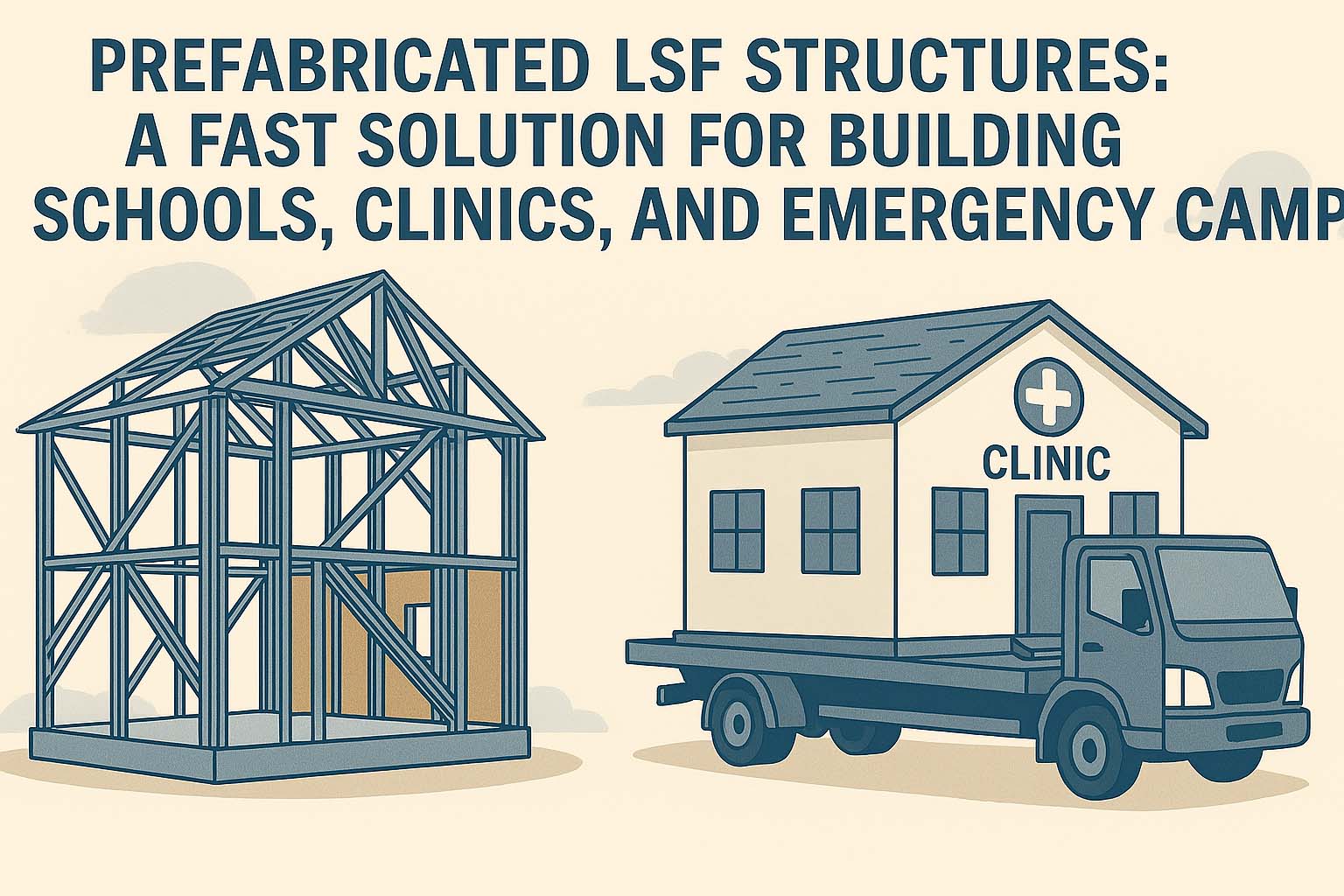
In times of urgent need—whether after natural disasters, in rapidly developing regions, or for temporary infrastructure—speed, flexibility, and durability become the top priorities in construction. Light Steel Frame (LSF) prefabricated structures offer an ideal solution for these scenarios, combining speed of assembly with high structural performance.
Why Choose LSF for Schools, Clinics, and Temporary Camps?
1. Rapid Construction
LSF components are prefabricated off-site with precision using specialized software and machinery. Once delivered to the site, the assembly process is fast, clean, and requires minimal labor. A fully functional school or clinic can often be erected in a matter of weeks instead of months.
2. Modular and Scalable Design
LSF buildings can be designed in modular units that are easy to transport, install, and expand. Whether it’s a single-classroom school or a fully equipped field hospital, the structure can grow based on evolving needs.
3. High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Despite being lightweight, LSF systems provide excellent structural performance, even in challenging environments. They are resistant to earthquakes, wind, and corrosion—making them especially suitable for remote or disaster-prone regions.
4. Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
When combined with proper insulation materials like rock wool or PIR panels, LSF buildings offer great thermal comfort and soundproofing, essential for schools and healthcare facilities.
5. Cost-Efficient and Sustainable
The efficiency of the prefabrication process reduces waste and lowers labor costs. Moreover, steel is recyclable, and the energy consumption during production and assembly is significantly lower compared to traditional building methods.
6. Compliance with International Standards
LSF structures can be designed and manufactured according to global engineering standards (such as Eurocode or AISI), ensuring safety, reliability, and long-term performance.
Applications in Real Life
- Emergency field hospitals and clinics during health crises
- Temporary classrooms in areas with growing student populations
- Accommodation units for refugees or disaster-displaced populations
- Construction site offices and worker camps
Conclusion
Prefabricated LSF structures are not only a fast and flexible building solution but also a reliable one. With the growing demand for efficient infrastructure around the world, LSF offers a forward-thinking approach to building smarter, faster, and more responsibly.
If you're planning a school, clinic, or camp project and need a quick yet robust solution, LSF is a choice worth considering.
When it comes to choosing a construction method, cost is always a critical factor. Light Steel Frame (LSF) construction has become increasingly popular due to its speed, precision, and efficiency—but how does it compare economically to traditional construction methods like reinforced concrete or masonry?
1. Material and Structural Cost
At first glance, the cost of steel components may appear higher than traditional materials like bricks or concrete. However, LSF systems are designed with precision, minimizing waste and excess material. Since the components are pre-engineered and manufactured with exact dimensions, there is almost no material loss on-site.
In many cases, the structural cost per m² of an LSF building is comparable or even lower than that of a conventional structure, especially when considering long-term savings.
2. Labor and Construction Time
One of the biggest advantages of LSF is the significant reduction in construction time. The pre-fabricated nature of LSF elements allows for fast assembly on-site, often reducing the overall build time by 30–50% compared to traditional methods.
This shorter timeline leads to lower labor costs, reduced site management expenses, and fewer delays due to weather or logistical challenges.
3. Foundation Savings
Because LSF structures are much lighter than concrete or brick systems, they require less massive foundations. This translates to lower excavation, concrete, and reinforcement costs—especially important in areas with poor soil conditions or seismic requirements.
4. Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
LSF buildings typically include high-performance insulation and dry wall systems, leading to superior thermal performance. This results in lower energy bills for heating and cooling throughout the building's life cycle.
5. Maintenance and Longevity
Steel frames are resistant to termites, rot, mold, and warping, unlike wood or poorly maintained concrete. As a result, maintenance costs over time are significantly reduced, and the overall durability of the structure is improved.
6. Final Verdict: Is LSF More Affordable?
While the initial cost of materials might be slightly higher, the overall cost-efficiency of LSF construction is superior when all factors are considered—especially for fast-track projects or locations with high labor costs.
By saving on labor, foundation work, energy consumption, and long-term maintenance, LSF often proves to be the smarter financial choice.
In recent years, the demand for modular structures and tiny houses has seen a significant rise. People are increasingly looking for affordable, flexible, and sustainable housing solutions that fit their lifestyles. One of the key materials driving this trend is Light Steel Frame (LSF), a construction method that offers numerous benefits for building modular and tiny homes.
What Makes LSF Ideal for Modular and Tiny Houses?
1. Lightweight and Strong:
LSF is made of cold-formed steel, which provides high strength while being significantly lighter than traditional steel or concrete. This makes it ideal for modular and tiny house construction, where weight and portability are crucial. LSF ensures that homes remain durable without compromising structural integrity.
2. Quick and Efficient Construction:
One of the main advantages of modular and tiny houses is the speed at which they can be built. With LSF, prefabricated panels are manufactured off-site and then assembled on-site. This not only reduces construction time but also minimizes disruptions to the environment, which is particularly important in areas with strict regulations or limited space.
3. Customizable Designs:
LSF allows for flexibility in design. Whether you're looking for a compact home or a more spacious modular unit, LSF can accommodate different layouts and architectural styles. Its adaptability makes it perfect for tiny houses, which often require efficient use of space without compromising on functionality or aesthetics.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Tiny houses and modular homes built with LSF benefit from the material's excellent insulation properties. The steel framing works well with various types of insulation, helping to create energy-efficient homes that stay warm in the winter and cool in the summer, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling systems.
5. Sustainability and Eco-friendliness:
As the world shifts towards more sustainable living, LSF is an excellent choice for eco-conscious builders and homeowners. Steel is 100% recyclable, making LSF homes more environmentally friendly compared to traditional building materials. Additionally, the compact nature of tiny houses reduces resource consumption, while LSF ensures that these homes are both energy-efficient and durable.
6. Real-World Applications of LSF in Tiny Houses
Many builders have already started incorporating LSF in tiny house projects due to its numerous benefits. These homes are often designed to be mobile, allowing homeowners to relocate easily. For example, modular tiny homes can be connected together to create larger living spaces or separated for mobility. With LSF’s lightweight nature, these homes remain transportable, while still maintaining structural strength.
Moreover, LSF’s resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and pests makes it an ideal material for long-lasting homes, even in challenging climates. The Future of Modular and Tiny House Construction with LSF As the need for affordable housing solutions continues to grow, the use of LSF in modular and tiny house construction is expected to expand. The flexibility, speed, sustainability, and strength of LSF will continue to make it a top choice for homeowners and developers seeking innovative solutions. By incorporating LSF into tiny homes and modular buildings, we're not just creating more livable spaces—we're shaping a future where homes are more sustainable, adaptable, and connected to the needs of modern life.